 Image credit: E. Romero
Image credit: E. Romero
Abstract
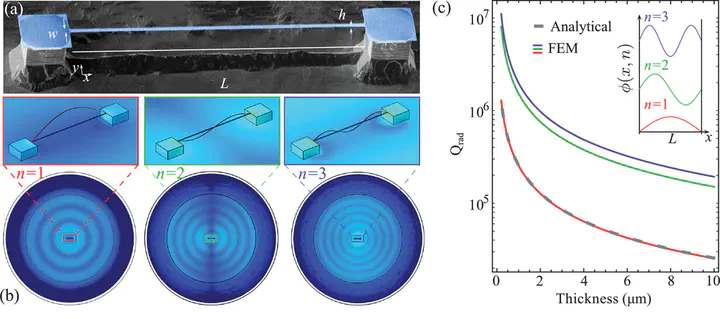
Nanomechanical resonators have applications in a wide variety of technologies ranging from biochemical sensors to mobile communications, quantum computing, inertial sensing, and precision navigation. The quality factor of the mechanical resonance is critical for many applications. Until recently, mechanical quality factors rarely exceeded a million. In the past few years however, new methods have been developed to exceed this boundary. These methods involve careful engineering of the structure of the nanomechanical resonator, including the use of acoustic bandgaps and nested structures to suppress dissipation into the substrate, and the use of dissipation dilution and strain engineering to increase the mechanical frequency and suppress intrinsic dissipation. Together, they have allowed quality factors to reach values near a billion at room temperature, resulting in exceptionally low dissipation. This review aims to provide a pedagogical introduction to these new methods, primarily targeted to readers who are new to the field, together with an overview of the existing state-of-the-art, what may be possible in the future, and a perspective on the future applications of these extreme-high quality resonators.